Supporting gut health with macroalgal extracts

Gut health has become increasingly important in the livestock industry with the emergence of antimicrobial resistance and the urge to limit the use of antibiotics. Macroalgal extracts can play an important role within the reduction of antibiotics use in farms.
The intestinal mucosa converges various functions: digestion and absorption of nutrients; as well as physical barrier against microbes and toxins thanks to the presence of a protective mucus layer and tight junction proteins that seal the paracellular space. The intestinal mucosa hosts both gut microbiota and immune cells (70% of the total number of immune cells are residents of the gut mucosa and gut-associated lymphoid tissue). In modern production systems, the gastrointestinal tract is being challenged and the subtle balance gut health relies on can be impaired. The components that define gut barrier and immune function can be weakened and lead to higher occurrence of digestive troubles associated with dysbiosis. This disbalance will trigger local and systemic inflammation, affecting the global health status and the growth performance of the animals. The challenge in the industry is to find solutions capable of supporting the epithelial barrier function and the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) in order to maintain a proper gut health and thus ensure good performance without the need of antibiotics.
Unique structural features
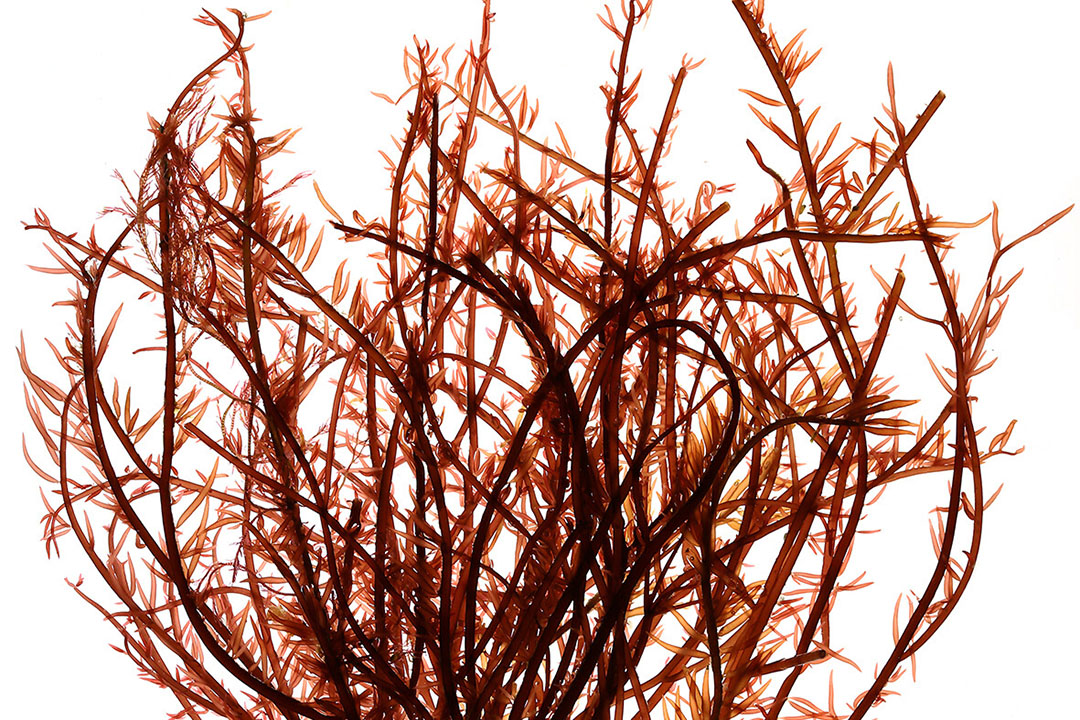
Parietal polysaccharides of seaweeds present structural complexity and a unique composition that confer them high reactivity and explain their biological properties when used in animals. The complexity and biological reactivity of seaweed polysaccharides derive from the nature of the sugar units, which are diverse and sometimes rare, such as uronic acids, xylose and rhamnose; the variety of glycosidic bonds leading to their branched structure and the presence of sulphate groups (Figure 1). Furthermore, their polyanionic structure and solubility increases their reactivity and facilitates their recognition by host cells. Sulphated polysaccharides are characteristic of macroalgae (they are not found in terrestrial plants, nor freshwater microalgae or yeast cell walls).
Figure 1 – Seaweed polysaccharides structure responsible of their high biological activities.

Olmix Group marine bioactive ingredient extraction know-how has led to the development of an in-feed product, Algimun, which is based on the combination of 2 bioactive macroalgal extracts: MSP Barrier, a red algal extract, which enhances the gut barrier function; and MSP Immunity, a green algal extract, that modulates innate and adaptive immune responses. Algimun bioactive molecules proved to be resistant to feed processing, especially to heat treatment and extrusion.
Gut health promoting properties
The effect of red algal extract on intestinal barrier function was assessed by measuring the expression of tight junction proteins and mucin-related genes using epithelial cell lines. Results showed that MSP Barrier upregulates the expression of genes that determine transmembrane (CLND-2) and scaffolding protein (ZO-1) synthesis which are essential for optimal functioning of the tight junction complexes. Moreover red algal extract upregulates the expression of genes that are necessary for the establishment of the mucus layer (MUC-2 and MUC-4) and the prevention of pathogen colonisation. It plays an important role in the maintenance of gut mucosa integrity by rendering the tight junctions stronger and promoting a more functional mucus layer. The extract strengthens gut integrity as observed by an increase in trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER) in IPEC-1 cell line incubated with a E.coli K88 1305. These findings were corroborated in an in vivo scientific study. MSP Barrier reduced the paracellular passage of FITC-dextran (gut permeability biomarker) to the blood stream in an animal model known to induce specific stress leading to an inflammation of the gut epithelium and consequently a higher degree of permeability (Figure 2).
Figure 2 – Evaluation of intestinal paracellular permeability in vivo (FITC-dextran levels in blood).

Supplementation of the red algal extract reinforced the intestinal barrier function of the gut epithelium which is the frontline of the innate immune defence against pathogens and toxins (significant reduction of the passage of the marker). A research project in collaboration with INRA (France) led to the demonstration of the effect of MSP Immunity on immune mediators’ transcription in an in vitro model (IPEC-1 cell line), including the identification of the metabolic pathways involved in this activation. Berri et al. (2016) first highlighted the green algal extract could positively influence the gene transcription of a broad array of immune mediators involved in defence mechanisms within the innate and the adaptive immune response, among others, the recruitment and activation of antigen-presenting cells, the differentiation and proliferation of lymphocytes B and lymphocytes T, while inducing immune tolerance thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties. In vivo scientific studies further confirmed the immunomodulating properties of MSP Immunity, namely by improving the defence activities of monocytes and heterophils in broiler chickens, by favouring the immune transfer through colostrum and milk from sow to piglet and by improving the phagocytic activity of macrophages and neutrophils in rainbow trout. MSP Immunity also upregulates the gene expression of immune mediators with anti-inflammatory activities in carp macrophages.
Combining macroalgal extracts
The benefits of Algimun during sensitive phases of the production cycle were assessed in the field in different animal species. Adding the supplement during the transition period in piglets (from day 21 until day 64) resulted in a lower inflammatory status (-16% haptoglobin level), a significantly lower percentage of animals needing a veterinary treatment (-57%, P<0.01) and improved live weight (+300g at the end of the trial) when compared to the control group. it also renders a high profitability: roi=”3:1.” the use of it in broilers has a positive effect on health parameters and growth performance. algimun reduces stress in animals as seen by a decreased heterophil to lymphocyte ratio and reinforces mucosal protection (higher level of immunoglobulin a). in short, red and green macroalgal extracts can be used as a natural alternative in-feed strategy to improve health and growth performance by reinforcing gut barrier function, supporting the development of the immune system in young animals and during challenges; and increasing the immune transfer from the mother to the progeny. by doing so, antibiotic use can be reduced.>
Author:
María García Suárez, For Feed Product Specialist, Olmix Group
References available on request